Omron’s new G5PZ-X PCB relay comes in a compact package with 20 A at 200 VDC rated load
All you need to Know about Heat Shrink Tubing and Sleeves

Heat shrink tubing is the method of covering or encasing the wires or cables in an insulating tube for protecting the wires from external disturbances. The Heat Shrink Tubing can also be called as Heat Shrink Sleeves. The process of heat shrinking is simpler than you think, the heat shrinks are available in wide ranges of size and color in the market, just get them from the market, insert the wire where you need the insulation and heat the sleeve.

Why should we use a Heat Shrink Tubing?
The heat shrink tube is used in different ways and purposes that focus on improving the protection, lifetime and maintenance of wires in a circuit.
Protect Wires and Cables from external factors:
The topmost usage of heat shrinking tubes is to offer protection to the wires and cables from abrasion, cutting, scuffing and low impact situations. The Heat Shrink act as a cable entry seal that can protect the wires from the environmental effects such as liquids like oil, water, and acids and also atmospheric factors, such as humidity and temperature that can cause damage to the wire. Some Heat shrinks are specially designed to be used in harsh environments and operate at even at -65°C to +260°C and can also act as good protection against water and moisture. The ATUM, CGAT, C-Wrap, Rayseal, HTAT, and SCL are some popular sleeves that can be used in harsh environments
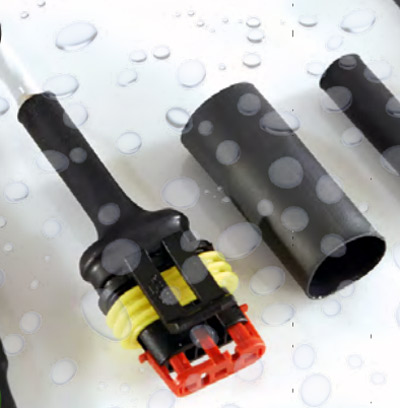

Insulating the Wires Properly:
There are no electrical circuits without connections; the Heat Shrinks are used to properly insulate those connections for better protection. Apart from insulating connections they are also used as an additional layer of protection to the wires as the basic insulation is not good enough. The Heat shrinks are available in various sizes for ensuring a perfect fit and it won’t come off with ages as compared with the other insulation solutions.

Reduce the Strains on the Wires:
The Electric wires and cables are often stretched and experiences strain due to insufficient space or length. These external tensions and wears might affect the life span of the wire, the heat shrinks can be used to reduce these strains and stress applied to the wire with the help of their durable nature. The below image shows a set of wires soldered to some connector pins. Here the heat shrink tubes not only covered the exposure of soldering but also provides mechanical support for the wires, by reducing the strain on connector pins.
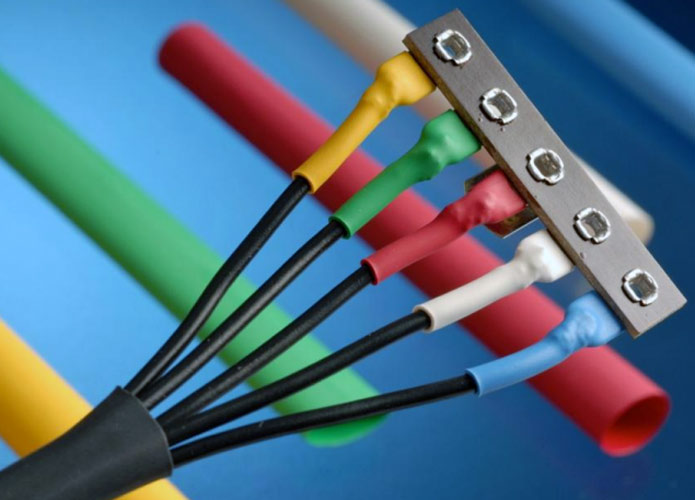
Used for bundling Cables:
A huge network of wires might be frustrating to every individual who works with the electrical system. The different sizes of the heat shrink allow you to bundle a group of wires together within a single tube. This is not only an aesthetic approach but also a good wire management technique that will be more helpful during the future maintenance of the system.

Rust Protection:
All the above uses are for an electrical system, in some special cases, the heat shrinks can also be used as rust protective in hardware like metal piping and welded joints. During the welding of stainless steel tubes the insulation coating might get depleted, in order to protect the welded joints from rust, the heat shrink tubes can be used. The adhesive layer in the heat shrinks merges perfectly to the metal surface and protect the pipelines from rust and other external disturbances.

Apart from these, the heat shrinks can also be used as a strain relief for color-coding specific components, identify various connections with the help of various colored tubes and change the texture and finishing of an object.
How to select an appropriate heat shrink?
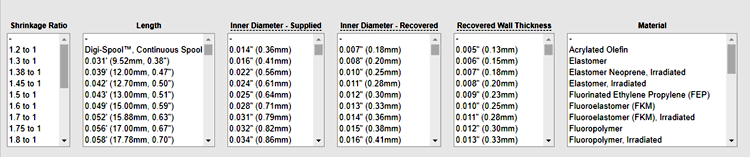
There are large varieties of heat shrinks available in the market in various types and sizes, for choosing the appropriate heat shrink you must consider the parameters like inner diameter, shrinkage ratio, Length, recovered wall thickness.
Choosing the inner diameter:
While identifying the inner diameter you should consider both the maximum and minimum perimeter of the object that you are going to cover. For better coverage, you should choose the shrink tube with an inner diameter with a 20-30% allowance that can provide the appropriate space for the heat shrink to merge along with the object tightly.

The Inner diameter-supplied (minimum inner diameter before heating) and the Inner diameter- recovered (Minimum inner diameter after heating) is the two important parameters you should consider while choosing Heat shrink tube’s inner diameter.
Choosing Shrinkage Ratio:
The Shrinkage ratio is the ratio between Inner diameter-supplied and inner diameter-recovered, the tubes are available in various ratio options like 2 to 1, 2.5 to 1, 3 to 1, etc. What the heat shrink ratio says is that the 2:1 Shrink tubes can shrink down to half of its original size, the 3:1 shrink tubes can shrink down to one-third of its original size. The shrink tube with a high shrinkage ratio is suitable for objects like connectors as it can encase the body of the connector and still be able to shrink down to a smaller diameter, like a wire or a cable.
Length of shrink tube:
While you are heating the shrink tube the length of the tube also gets reduced 5-7%, so you should choose a shrink tube that is a bit longer than you need.
The thickness of the Shrink tube:
Generally, the thickness of an object gets reduced if it is stretched, the more you stretch the thinner the object gets. In the case of a shrink tube, it is vice versa, as the tube is shrunk down the thickness of the tube increases. So, look at the datasheet of the heat shrink tubing and choose the best thickness that suits the environment of your application.
Apart from these parameters, you must also carefully choose the material, working temperature and shrinkage temperature as they denote the features of the heat shrink tube. The heat shrink tubes are available for all kinds of cables associated with both high and low power applications, know your application better and choose the appropriate heat shrink tube for it.
Materials used for making heat shrinks
Polyolefin:
The most popular material used for making heat shrinks is Polyolefin. The Polyolefin based material has lots of advantages over other types of heat shrinks. They are Flexible, fast shrinking, excellent durability, high flame retardant, high UV resistance, Excellent chemical and Electrical properties. The Polyolefin heat shrink has a shrinking temperature of 100°C and withstands a high temperature of 125°C - 135°C. These types of heat shrinks are mostly used for mechanical protection, insulation, and marking.

PVC:
The Polyolefin heat shrinks are comparatively costly to be used in all kinds of applications, for applications where the budget matters you can use the PVC heat shrinks. The PVC heat shrinks cost 10% to 50% less than the Polyolefin heat shrinks. These heats shrink are made up of Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), they can’t withstand higher temperature like Polyolefin but has the ability to withstand a reasonable maximum temperature of 105°C.

The PVC heat shrinks are available in various colors and if you want transparent shrink tubes are also available. They are available in flame-retardant versions and have a better tensile strength and abrasion resistance than the Polyolefin heat shrinks.
Adhesive lined heat shrinks:
The Adhesive lined heat shrink consist of two layers, the outer layer is made up of Polyolefin and the inner layer is made up of adhesive that melts and flows at the same temperature at which the outer layer starts shrinking. The adhesives flow and fill the voids and settle at the shape of the object to be tubed. Once the adhesives are cooled it acts as an environmental seal and protects the sealed object from moisture and other disturbances.
Other materials:
The heat shrinks are also available in other materials such as PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), FEP (Fluorinated ethylene propylene), PVDF (polyvinylidene difluoride), elastomers, Silicon rubber, Viton, and other special materials. The use of each type of material depends on the environment that they are to be used and their properties.












