ATMega8 - 8bit AVR Microcontroller
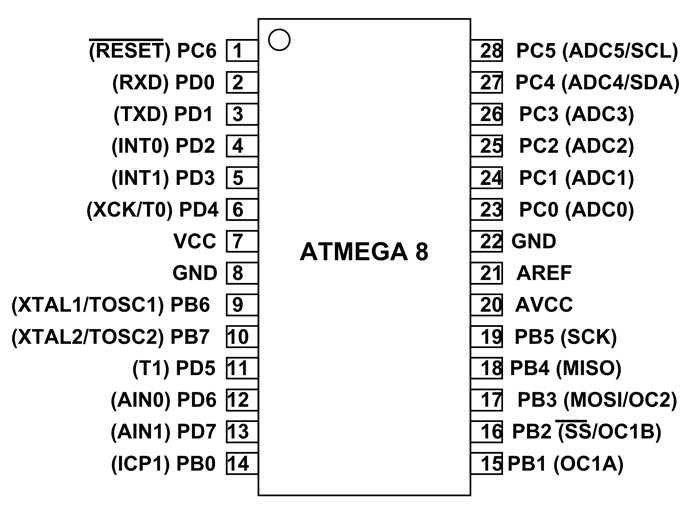
ATMEGA8 Pin Configuration
|
Pin No. |
Pin name |
Description |
Alternate Function |
|
1 |
PC6 (RESET) |
Pin6 of PORTC |
Pin by default is used as RESET pin. If the RSTDISBL Fuse is programmed, PC6 can be used as an I/O pin. (Pulled HIGH to RESET controller) |
|
2 |
PD0 (RXD) |
Pin0 of PORTD |
RXD (USART Input Pin)
USART Serial Communication Interface [Can be used for programming] |
|
3 |
PD1 (TXD) |
Pin1 of PORTD |
TXD (USART Output Pin)
USART Serial Communication Interface [Can be used for programming]
INT2( External Interrupt 2 Input) |
|
4 |
PD2 (INT0) |
Pin2 of PORTD |
External Interrupt INT0
|
|
5 |
PD3 (INT1) |
Pin3 of PORTD |
External Interrupt INT1
|
|
6 |
PD4 (XCK/T0) |
Pin4 of PORTD |
T0( Timer0 External Counter Input) XCK ( USART External Clock I/O) |
|
7 |
VCC |
|
|
|
8 |
GND |
|
|
|
9 |
PB6 (XTAL1/TOSC1) |
Pin6 of PORTB |
XTAL1 (Chip Clock Oscillator pin 1 or External clock input) TOSC1 (Timer Oscillator pin 1) |
|
10 |
PB7 (XTAL2/TOSC2) |
Pin7 of PORTB |
XTAL2 (Chip Clock Oscillator pin 2) TOSC2 (Timer Oscillator pin 2) |
|
11 |
PD5 (T1) |
Pin5 of PORTD |
T1(Timer1 External Counter Input) |
|
12 |
PD6 (AIN0) |
Pin6 of PORTD |
AIN0(Analog Comparator Positive I/P)
|
|
13 |
PD7 (AIN1) |
Pin7 of PORTD |
AIN1(Analog Comparator Negative I/P)
|
|
14 |
PB0 (ICP1) |
Pin0 of PORTB |
ICP1(Timer/Counter1 Input Capture Pin) |
|
15 |
PB1 (OC1A) |
Pin1 of PORTB |
OC1A (Timer/Counter1 Output Compare Match A Output) |
|
16 |
PB2 (SS/OC1B) |
Pin2 of PORTB |
SS (SPI Slave Select Input). This pin is low when controller acts as slave. [Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming]
OC1B (Timer/Counter1 Output Compare Match B Output) |
|
17 |
PB3 (MOSI/OC2) |
Pin3 of PORTB |
MOSI (Master Output Slave Input). When controller acts as slave, the data is received by this pin. [Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] OC2 (Timer/Counter2 Output Compare Match Output) |
|
18 |
PB4 (MISO) |
Pin4 of PORTB |
MISO (Master Input Slave Output). When controller acts as slave, the data is sent to master by this controller through this pin.
[Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] |
|
19 |
PB5 (SCK) |
Pin5 of PORTB |
SCK (SPI Bus Serial Clock). This is the clock shared between this controller and other system for accurate data transfer. [Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] |
|
20 |
AVCC |
Vcc for Internal ADC Converter |
|
|
21 |
AREF |
Analog Reference Pin for ADC |
|
|
22 |
GND |
GROUND |
|
|
23 |
PC0 (ADC0) |
Pin0 of PORTC |
ADC0 (ADC Input Channel 0) |
|
24 |
PC1 (ADC1) |
Pin1 of PORTC |
ADC1 (ADC Input Channel 1) |
|
25 |
PC2 (ADC2) |
Pin2 of PORTC |
ADC2 (ADC Input Channel 2) |
|
26 |
PC3 (ADC3) |
Pin3 of PORTC |
ADC3 (ADC Input Channel 3) |
|
27 |
PC4 (ADC4/SDA) |
Pin4 of PORTC |
ADC4 (ADC Input Channel 4) SDA (Two-wire Serial Bus Data Input/Output Line) |
|
28 |
PC5 (ADC5/SCL) |
Pin5 of PORTC |
ADC5 (ADC Input Channel 5) SCL (Two-wire Serial Bus Clock Line) |
ATMEGA8 Features
|
ATMEGA8 –Simplified Features |
|
|
CPU |
8-bit AVR |
|
Number of Pins |
28 |
|
Operating Voltage (V) |
+2.7 V TO +5.5 V (ATmega8L) +4.5 V TO +5.5 V (ATmega8) (+5.5V being absolute maximum) |
|
Number of I/O pins |
23 |
|
Communication Interface |
Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface(16,17,18,19 PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller] Programmable Serial USART(2,3 PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller] Two-wire Serial Interface(27,28 PINS)[Can be used to connect peripheral devices like sensors and LCDs] |
|
JTAG Interface |
Not available |
|
ADC Module |
6 channels , 10-bit resolution ADC |
|
Timer Module |
Two 8-bit counters, One 16-bit counter [Total three] |
|
Analog Comparators |
1 |
|
DAC Module |
Nil |
|
PWM channels |
3 |
|
External Oscillator |
0-8MHz for ATMEGA8L 0-16MHz for ATMEGA8 |
|
Internal Oscillator |
0-8MHz Calibrated Internal Oscillator |
|
Program Memory Type |
Flash |
|
Program Memory or Flash memory |
8Kbytes[10000 write/erase cycles] |
|
CPU Speed (MIPS) |
16 MIPS |
|
RAM |
1KBytes |
|
EEPROM |
512 |
|
Watchdog Timer |
Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator |
|
Program Lock |
Yes |
|
Power Save Modes |
Six Modes[Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, Power-down, Standby and Extended Standby] |
|
Operating Temperature |
-55°C to +125°C(+125 being absolute maximum, -55 being absolute minimum) |
Note: Complete technical information can be found in the ATMEGA8 Microcontroller Datasheet linked at the bottom of this page.
ATMEGA8 Replacements
ATMEGA8 Alternatives
ATMEGA16, ATMEGA32, ATMEGA8535
Other 8-bit Microcontrollers
Where to use ATMEGA8 Microcontroller
ATMEGA8 is a 28 pin AVR microcontroller. Although we have many similar microcontrollers, ATMEGA8 is popular because it is one of the cheapest microcontroller and provides many features in lesser pins. With program memory of 8Kbytes, ATMEGA8 application is very versatile. With various POWER SAVING modes, it can work on MOBILE EMBEDDED SYSTEMS. With its compact size, it can be put in many small boards. With Watchdog timer to reset under error, it can be used on systems with minimal human interference. These features added together in one controller make the ATMEGA8 popular.
How to Use ATMEGA8 Microcontroller
Using ATMega8 is similar to other ATMega microcontrollers, such as ATMega32. Similarly, the micro-controller need to be programmed and added appropriate peripherals to get the output. Without programming the controller is an empty chip.
For working of ATMEGA8, first we need to burn the appropriate program file in the ATMEGA8 FLASH memory. After dumping this program code, the controller executes this code and provides appropriate response.
Entire process of using an ATMEGA8 goes like this:
- List the functions to be executed by ATMEGA8.
- Write the functions in programming language in IDE programs. You can download the IDE program for free. IDE program for AVR controllers is ‘ATMEL STUDIO’. Link for ATMELSTUDIO is given below.
(Usually Atmel Studio 6.0 for Windows7 [ http://atmel-studio.software.informer.com/6.0/ ],
Atmel Studio 7 for Windows10 [ https://www.microchip.com/avr-support/atmel-studio-7 ])
(Remember for these IDE the program should be written in ‘C’ language)
- After writing the desired programs compile to eliminate errors using IDE.
- Make the IDE generate HEX file for the written program.
- Choose the programming device (usually SPI programmer made for AVR controllers) which establishes communication between PC and ATMEGA8.
- Run the HEX file burning software which is provided to the chosen programming device.
- Choose the appropriate program HEX file in the SPI or other programmer software.
- Burn the HEX file of written program in ATMEGA8 flash memory using this program.
- Disconnect the programmer, connect the appropriate peripherals for the controller and get the system started..
Applications
There are hundreds of applications for ATMEGA8.
- Industrial control systems.
- SMPS and Power Regulation systems.
- Analog signal measuring and manipulations.
- Embedded systems like coffee machine, vending machine.
- Motor control systems.
- Display units.
- Peripheral Interface system.
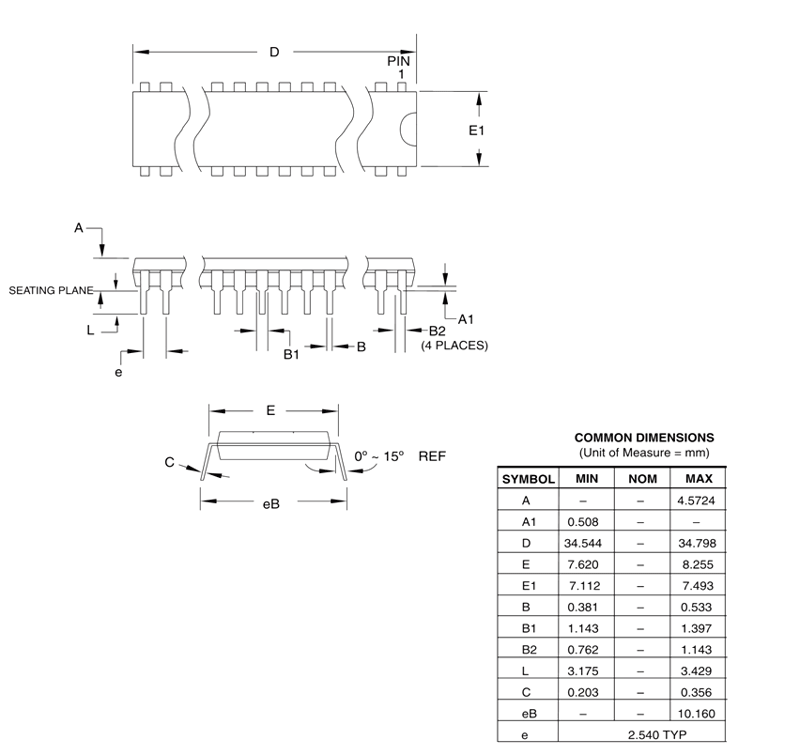
2D Model and Dimensions
All measurements are in millimeters.